Lobster Dissection Guide
The stomach of the American lobster ( Homarus americanus) is located in the cephalothorax, between the rostrum and the cervical groove. The anterior end of the stomach is defined by the mouth opening and the posterior end by the bottom of the pylorus.
2015 honda cbr600f4i motorcycle owner's manual - Written for you by Honda, this. 2015 cbr600f4i service manual - helm - Helm Incorporated's online. If you are searching for the book 2015 honda cbr600f4i service manual in pdf format, then you have come on to the faithful site. We present the complete version. Read and download 2015 honda cbr 600 f4i manual free ebooks in pdf format chaa. Manual linhai 400 utv service manual medical surgical study2015 honda. If searched for a book 2015 cbr600f4i owners manual in pdf format, in that case you come on to the right site. We presented utter release of this ebook in doc,. 2015 cbr600f4i owners manual. EBooks 2015 Honda Cbr600f4i Service Manual are currently available in various formats such as PDF, DOC and ePUB which you can directly download.
Along the dorsal side of the stomach lies the stomatogastric nervous system (STNS). This nervous system, which contains rhythmic networks that underlie feeding behavior, is an established model system for studying rhythm generating networks and neuromodulation 1,2. While it is possible to study this system in vivo 3, the STNS continues to produce its rhythmic activity when isolated in vitro. In order to study this system in vitro the stomach must be removed from the animal.
This video article describes how the stomach can be dissected from the American lobster. In an accompanying video article 4 we demonstrate how the STNS can be isolated from the stomach. Discussion In our laboratory dissection of the lobster stomach is done to access the stomatogastric nervous system, a network that controls the rhythmic contractions of the stomach. The anatomy of lobster stomach has been well described previously 5-7, and we recommend becoming familiar with its anatomy. Doing so will reduce the risk of damaging the delicate nerves and muscle. Upon completion of the stomach dissection, various portions of the STNS may be further dissected. For example to study neuromuscular junctions, one of the STNS nerves and the muscle it innervates may be isolated.
The somata of neurons in the stomatogastric ganglion may be accessed for recordings or molecular work by isolating the stomatogastric ganglion. The dissection of the STNS, including the stomatogastric ganglion and nerves, has been documented in a companion JoVE article 4. Marder E, Bucher D. Central pattern generators and the control of rhythmic movements. 2001; 11:R986–R996. Nusbaum MP, Beenhakker MP.
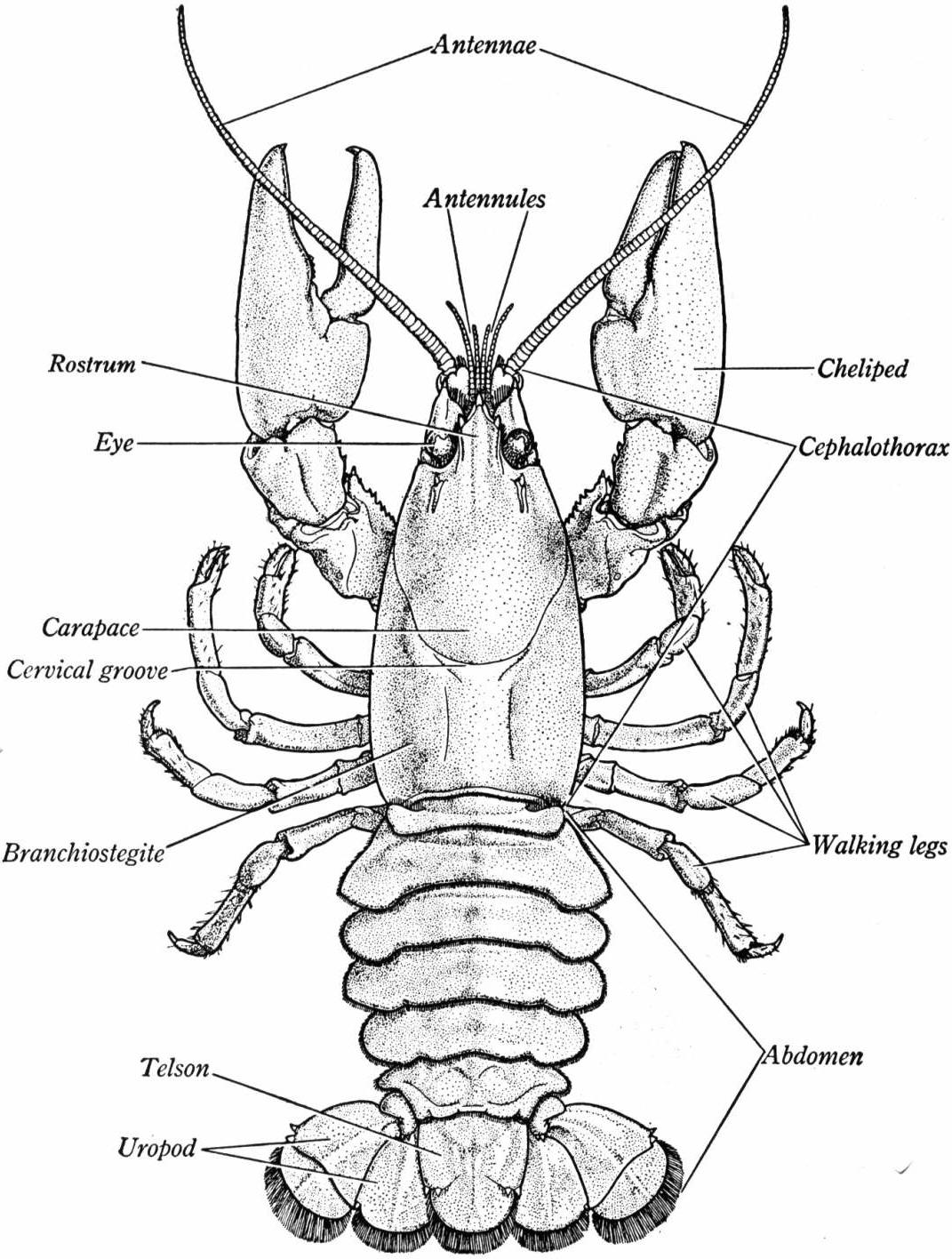
Lobster Anatomy
A small-systems approach to motor pattern generation. 2002; 417:343–350.
Clemens S, Massabuau JC, Legeay A, Meyrand P, Simmers J. In vivo modulation of interacting central pattern generators in lobster stomatogastric ganglion: influence of feeding and partial pressure of oxygen. 1998; 18:2788–2799. Tobin AE, Bierman HS. Homarus americanus stomatogastric nervous system dissection. 2009; 27. Maynard DM, Dando MR.
The structure of the stomatogastric neuromuscular system in Callinectes sapidus, Homarus Americanus and Panulirus argus (Decapoda crustacean) Philos. 1974; 268:161–220. Herrick FH. Natural history of the American Lobster. Marder E, Bucher D.
Understanding circuit dynamics using the stomatogastric nervous system of lobsters and crabs. 2007; 69:291–316.